In 2023, we have seen 3D printing becoming bigger, faster and cheaper. Uscribe now includes 3D printers in our catalogue, with the new 3D printing darling Bambu Lab heading the charge. This sets the stage for what promises to be an even more transformative year in 2024. Here are some of the trends we’re going to look out for in the new year.
1. Multi-material 3D printing
As we enter 2024, the demand for intricate and functional prototypes is on the rise. Imagine producing a prototype with rigid and flexible components seamlessly integrated into a single design. Multi-material 3D printing opens up avenues for manufacturing complex, multi-component objects in a single printing process, saving time and resources. Whether it’s creating prototypes for consumer products or functional parts for machinery, Bambu Lab’s multi-material capabilities using its AMS (Automatic Material System) offer a versatile solution for businesses looking to push the boundaries of design and functionality.
Bambu Lab’s X1 Carbon 3D Printer is able to print with exceptional thermal resistance and with the simultaneous use of multiple materials in a single print job. Bambu Lab also features polycarbonate and carbon fibre filament for strong, durable prototypes.
Incorporating multi-material 3D printing into your workflow not only enhances the visual appeal of your creations but also allows for the production of more realistic and functional prototypes.
2. The Rise Of 3D Printing’s Middle Class
One noteworthy trend that’s taking center stage is the rise of 3D Printing’s middle class, where an emergence of great quality mid-range machines are reshaping the landscape. Instead of asking “why” 3D printing should be adopted and accepting cheaper, mediocre machines and materials, it now is a matter of “how” we can use 3D printing to scale our businesses or improve our lifestyle without breaking the bank. The accessibility of affordable yet high-quality 3D printers is democratising the technology, empowering a broader range of businesses to harness the benefits of additive manufacturing.
Bambu Lab’s affordable yet high quality open frame P1P 3D printer doesn’t cut corners on exceptional output, and its high-speed 3D printing goes up to 20,000 mm/s² acceleration.
3. Sustainable Materials Revolution
Bambu Lab actively incorporates biodegradable filaments sourced from renewables and integrates recycled polymers into its 3D printing processes, signaling a move towards reduced dependence on virgin plastics and a smaller environmental footprint. The introduction of plastic granulators adds efficiency to the recycling aspect of Bambu Lab’s 3D printing, establishing a closed-loop system to curtail waste.
Plastic granulators, like the one from Clarke, allows for the efficient recycling of failed prints, excess materials from 3D printing (spaghetti monsters, anyone?) or even discarded plastic products. It grinds these plastic waste down to smaller granules so that it can be used to form sheets or even filament.
Bambu Lab also encourages users to either reuse their existing filament spools or print one (to be reused).

These sustainability efforts are in line with the evolving trends in the 3D printing sector, specifically in addressing environmental concerns.
4. Robotic Arms in Additive Manufacturing
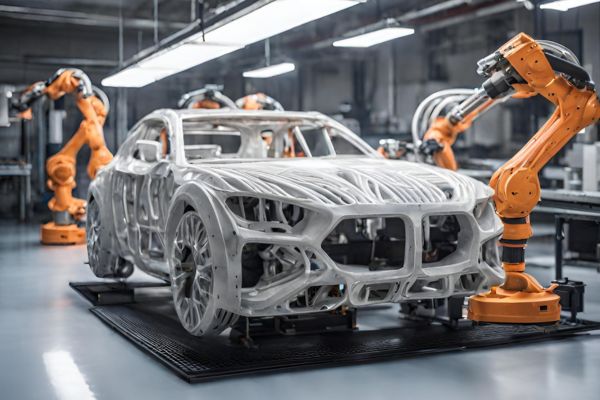

With the upscaling of additive manufacturing for businesses, there is a transformative trend of robotic arm 3D printing to enable precision and intricacy in design that was previously unattainable. Dobot robotic arms, especially the CR series, are created for industrial use to seamlessly navigate complex patterns to reach unprecedented levels of accuracy and efficiency in their operational processes.
Robotic arms can enhance scalability and customisation by being deployed in an array, simultaneously working on different parts of multiple identical objects. This allows mass customisation without sacrificing efficiency. Robotic arms, with their increased degrees of freedom, can manipulate the print head or nozzle to print complex geometries or overhangs.
The 3D printing landscape is undergoing a significant transformation as we move from 2023 to the promising year of 2024. Not only is 3D printing becoming bigger, faster, and more affordable, but it is also embracing transformative trends that redefine its applications. From multi-material 3D printing, exemplified by Bambu Lab’s innovative AMS technology, to the democratization of 3D printing with the rise of the middle class, the industry is evolving rapidly. Sustainable practices, including the use of biodegradable filaments and recycled polymers, are at the forefront, aligning with global environmental efforts. The integration of robotic arms, such as Dobot’s CR series, signifies a shift towards precision and intricacy, enhancing scalability and customization in additive manufacturing. Let’s bring on 2024 and see what else it has to offer in the realm of 3D printing!
